Ensuring the water quality standards are on par is a critical responsibility of all water utility service enablers worldwide. Public water service establishments rely on a myriad of technological capabilities to ensure the water quality of potable water is on point before it is reticulated to the consumers’ taps. However, the traditional fragmented systems used by water utility service providers have led to suboptimal water treatment asset management, which results in failing to treat contaminated water optimally.
This article will discuss how water treatment asset management is facilitated by new technologies and how modern water treatment facilities are utilising these technologies to overcome a multitude of inconveniences.
Why is Recycled Water Important?
- Cooling down power plants
- Dust control strategies in urban areas
- Fire Suppression
- Industrial uses like diluting, sanitation, washing and processing purposes
- Large-scale farming purposes like mechanised centre-pivot irrigation systems, sprinklers, furrow irrigation, drip watering and more
- Plumbing systems
- Public pools
- Water systems used in recreational parks and wildlife corridors
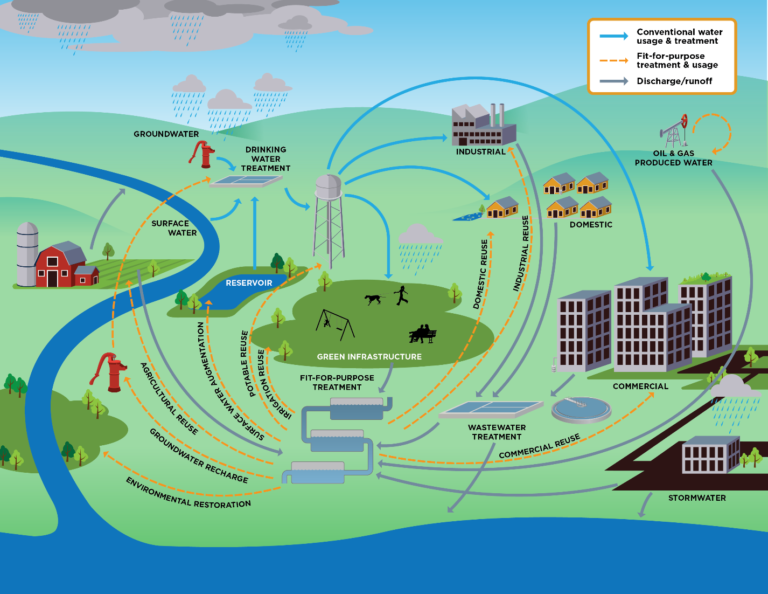
epa.gov
Water Treatment Asset Management and New-Age Technologies
- Control Boxes
- Filters
- Gauges
- Hydrostatic flanges
- Inlet Lines
- Lab Equipment
- Overflow sewers
- Pumps
- Tanks
- Valves and more
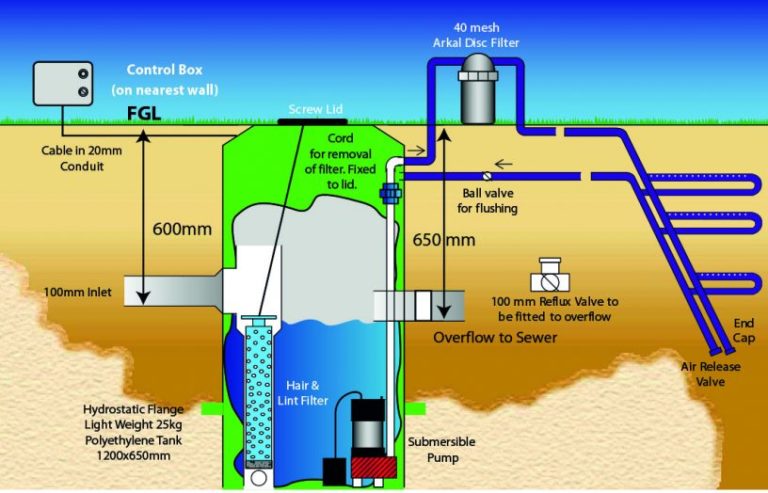
renew.org.au
AI-powered Advanced Analytical Technologies
Any industrial practitioners never underestimate the power of AI (Artificial Intelligence); just like in other industrial domains, AI is the core of optimising the Water Treatment Plant Asset Management. The AI technology allows AI models that are trained with real-time and historical data to detect noteworthy asset performance, operative conditions, risks, threats and other inconveniences in pre-time. The treatment facility is rigged with smart sensors interconnected to all systems by the power of IIoT technology; therefore, all asset behaviours will be assessed, diagnosed and coordinated by the asset managers using a centralised system. It connects the data systems to the water quality-check laboratories, communication systems of experts, historical systems, real-time data hubs and more. This system allows them to look at AI degradation curves and predictive models that represent all asset events in factual visual representations.
For example, if treatment pump A is connected to sensor A1 and sensor A2, A1 and A2 would detect that the pump engine vibrates unhealthily, by the time the vibration level surpasses a predetermined level, the sensor will send a notification to the user saying the pump is performing suboptimally. It will also predict what will happen if the pump is not maintained on time.
Digital Twin Technology
This is one of the newly-fangled technologies that have influenced the asset management strategies of the water recycling facilities. This technology allows the asset managers to view a physical element- a machine, infrastructure, valve, pump, compressor etc.- or a system the treatment facility at large- via a virtual representation of the structural model and the dynamics of its physical counterpart. It is a visualisation luxury that any asset manager can use to tweak a digital replication of an asset to view all the operational and structural parameters in real-time.
For example, they can use this technology to view all the asset performance of individual assets of a treatment facility. They can view the real-time OEE levels, water quality levels, asset integrity levels, schedules and other data related to the facility under one glass pane.
Simulation Platforms
- Natural occurrences (Blue-green Algaes, Red Tide, Ph values, Nitrogen levels, phosphorus levels, dissolved oxygen levels, etc.
- Disasters (floods, landslides, wildfires, storms and more), and
- Human-made disasters (pollution, dumping, industrial waste discharge and more). All these contaminations complicate the water treatment facility levels.
The Future of Water Treatment Asset Management Continues to Optimise
Even though water recycling practices are considered an integral part of the water production systems, it is soon becoming a fourth water utility sector amongst stormwater, drinking water and wastewater assets. This is due to the complex water recycling asset categories that need much attention in streamlining recycled water services while earning the public trust of communities that consume reclaimed water. This is why treatment asset management is a keen and serious responsibility for all water utility service enablers.
New-age technologies, as defined by industry 4.0, demands to keep rerouting the path to the future of optimised water treatment facilities to be more data-pointed, faster, reliable and efficient at the same time. Being in the loop of these technological advancements gives every water treatment specialist the advantage of investing in the right technology to ensure that their treatment assets are in their best condition and performance capacities throughout their life cycles.







