Do you know that the invention of two major systems changed the whole infrastructure process drastically over the years? So, what are these technologies? With the use of computer-aided design or commonly known as CAD technology, precise and accurate drawings as well as 2D and 3D models can be developed for a range of technical purposes. Geographic Information Systems or GIS, on the other hand, is a technology that helps people in the construction business understand geospatial connections by organising, analysing, and visualising geographical data.
Are they too complicated to understand? When it comes to the major difference between these two technologies, CAD is occupied before starting the project as a model of data visualisation and GIS has been employed after the project is well-established. As CAD puts more emphasis on the design, GIS provides a vivid exploration of its geographic data. Both of these technologies are crucial for building infrastructure, yet the utilisation of them are drastically different. When moving out of traditional methods, these two fill the gaps in infrastructure management. In this article, we will explore how this process happens and the pros and cons of each technology for building infrastructure.
Real-life Challenges in Traditional Building Infrastructure Management

Before moving on to the above-mentioned two main technologies, we will discover the challenges faced by authorities when getting stuck with traditional building infrastructure management. It’s always important to understand why you need to opt for new technology.
Low Connectivity
Since the traditional building infrastructure system usually employs proprietary protocols, connecting to other systems and devices can be quite challenging. This disconnect with more contemporary technologies can be rather restricting as it prevents the movement of data between computers. This might be particularly problematic when concerning how reliant on technology the modern world is.
Poor Data Management
When it comes to traditional building infrastructure management, authorities have to collect data manually. This method is time-consuming and since it is done manually, it is prone to many errors. Also, the data is kept in silos which makes it difficult to access and analyse through various other platforms. No integration with data storage is the reason behind this.
Limited Reporting Options
The traditional building infrastructure approaches’ inability to generate informative data on vital factors like system performance and energy use is a serious drawback. This constraint makes it very challenging to identify systemic inefficiencies, which makes it challenging to implement the required remedial steps.
Low Scalability
Poorly designed traditional infrastructure won’t be able to handle the volume of data that building equipment, electronics, and sensors will create. These data infrastructure problems result in unexpected and even problematic data flows, which makes it challenging for system integrators to scale up or down systems.
High Upkeep Expenses
The complex nature of traditional building infrastructure necessitates regular, costly upkeep and alterations. Its dependency on certain software and technology makes it more challenging to find replacement parts or support, which exacerbates issues.
Introduction to CAD
First, let’s discover what CAD is. Designers, architects, and engineers can build and change complex designs in both 2D and 3D forms. With this advanced software, projects can easily be seen from a variety of angles and viewpoints, allowing for a thorough comprehension of the infrastructure or product being built. So, if put in simple words, it is the employment of computer software to design new products in 3D.
Pros
Lower Costs for Design Production
Through precise virtual modelling and simulations, it has the benefit of lowering manufacturing costs by allowing designers to find flaws and fix them before production starts. This prevents material waste and costly blunders. A crucial tool for businesses looking for optimum solutions, the latter also eliminates the need for physical prototypes and facilitates quick design updates, enabling cost efficiency and profitability.
Growth in Productivity
The design process is completely transformed by this software, allowing for cost savings and a speedier turnaround on projects. It enables smooth idea testing, digital archiving, and increased product flexibility in comparison to time-consuming manual approaches. Efficiency gains enable fewer teams to produce outstanding results at affordable prices. This is a useful tool for streamlining the design and manufacturing processes, which ultimately saves time and money.
No Space for Errors
Errors are the most fearful aspect of infrastructure. Do you agree? When compared to manual design methods, CAD offers several benefits, particularly when it comes to creating bills of materials. These benefits include reducing mistakes and increasing productivity. Furthermore, the software is made to anticipate and avoid typical design errors, improving the overall accuracy and calibre of the finished product.
Not Compromising on Quality
Flexibility is one requirement of design where you will need some advanced technology like CAD. Designers have the freedom to easily return and edit their designs thanks to this software, which gives them the flexibility to fix mistakes.
Cons
Too Expensive
This is not a system where you can purchase anywhere anytime. It requires spending and investing a huge amount of money on this system as CAD comes with a lot of integration and features.
Requirement for a Skilled Workforce
Not everybody is able to handle this technology and it needs to have a skilled workforce to gather data from the system, understand them, and interpret these complex designs into understandable drawings.
Difficult to Keep Up with Constantly Changing and Improving Technology
It might be challenging to remain up to date with CAD given how rapidly technology advances. The constant need for learning and flexibility is brought on by new features, regular upgrades, and changing trends. Designers and engineers must invest time and energy to stay current on new advances in order to fully utilise the capabilities of it.
Introduction to GIS
The concept of “GIS” refers to a potent computer-based system that makes it easier to store, retrieve, manipulate, analyse, and manage geographic data that involves actual places and surfaces. This helps users to view, analyse, and comprehend the intricate links between geographic objects and their qualities by combining multiple forms of spatial information, such as maps, satellite images, and geospatial data.
Pros
Geospatial Data Visualisation
Latter provides engineers and authorities with a significant edge by facilitating the comprehension and display of geographical data. This data could be visualised as maps and other visual representations and includes a wide range of information, such as demographic and climate-related data.
Improve Planning
GIS acts as a platform for storing and analysing enormous volumes of data, playing a critical part in the planning and decision-making processes. Utilising this data, it enables authorities to make educated judgments on a variety of issues.
Strengthening Emergency Response Capabilities
It provides in-the-moment information on the location and scope of an emergency, allowing emergency workers to assess the situation quickly and take appropriate action.
More Emphasis on Environmental Management
GIS is now an essential tool in environmental management for comprehending and reducing the effects of human activity on the environment. It helps users to acquire insights into the consequences of deforestation, a substantial contributor to climate change, by storing, analysing, and displaying environmental data.
Cons
Not So Budget-Friendly
Companies who want to benefit from this software’s powerful geographic analytical and data management capabilities must invest a lot of money because it is recognized for being pricey.
Requirement for a Large Volume оf Data
In order to use GIS for activities, a huge amount of data input needs to be provided. The considerable data processing does raise the chance of errors, however, it is important to closely check the accuracy and reliability of the system’s outputs.
Resolution Issues
This can encounter relative resolution loss while dealing with huge amounts of data or doing geographic analysis, which might affect the precision and depth of information representation in specific applications.
Similarities and Dissimilarities of CAD and GIS
Now that we have covered all the features of these technologies, let us move to the similarities and dissimilarities of them.
Similarities
- Both are computer-based technologies for data management
- Employment of spatial data to fulfil the requirement
- Involves in digital creation and visualisation of data
- Analyse data
- Provides comprehensive view
- Integration with other software
- Offer a visual representation of objects or landscapes in detail
- Both pave the way to stimulate real-world scenarios in digital format
- Result in data-driven decision making
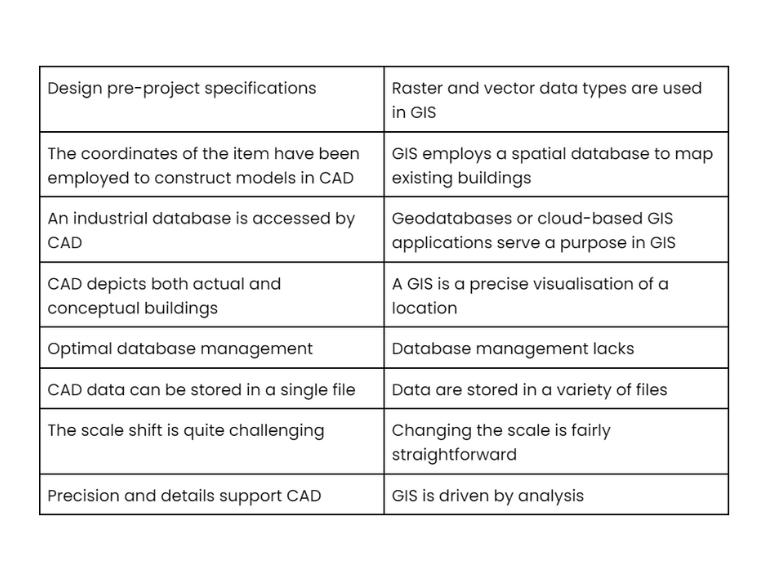
Dissimilarities of CAD and GIS
CAD or GIS: The Decision is Yours

Now that you know, there are certain infrastructure-related features that CAD and GIS cover. Your particular demands and goals will ultimately determine whether you choose CAD or GIS. Whether it is handling geographic data or constructing infrastructure, each technology has its own advantages and applications. You can decide on a course approach that most closely reflects your objectives by analysing your requirements and taking into account the benefits each option offers.







