Roads have become one of the most common and certain elements of people’s lives as they are everywhere, and no surprise that many do not feel like giving special importance to them. Yet, they miss the fact that every other task in their lives depends on one thing, which is transportation. Without roads, there will be no transportation.
One of the major challenges road development authorities and municipalities encounter when handling road networks is that they are prone to cracking. Road cracks seem to be less problematic at first glance, but the worst occurs if the authorities keep ignoring them. It will lead to some safety issues and costly repairs.
This article covers everything about road cracks, reasons for them, risks and consequences, and most importantly, some practical tips to prevent them.
What are Road Cracks?
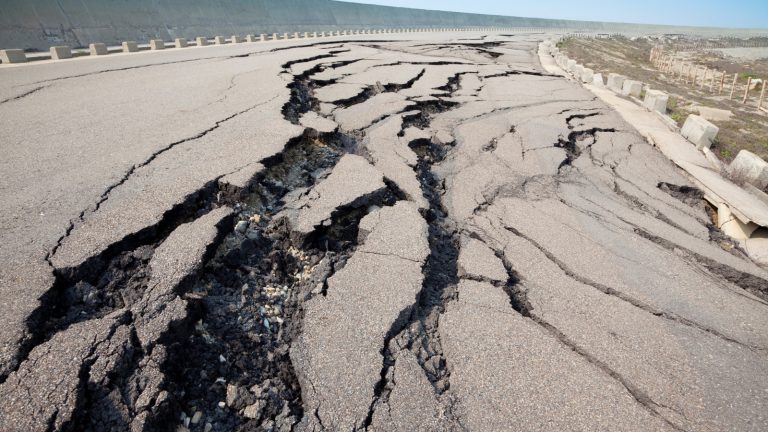

Road cracks are known to be the fractures or splits that exhibit progression confined to the surface domain of asphalt or concrete pavement. They characteristically present as patterned formations and can range in size from tiny fissures to large gaps.
These fissures are liable to culminate in more pronounced developments within a short time, and they are also signals that the pavement is deteriorating or under stress.
Common Types of Cracks

If you look into the road cracks, you will notice there are several types. Each type stems from different causes, such as:
Fatigue (Alligator) Cracks: These are known as a network of interlinked cracks that looks similar to the skin of an alligator. The main reason that leads to this type of crack has been identified as persistent traffic stress.
Block Cracks: These cracks occur due to the asphalt’s ageing and deterioration, and they appear as large, rectangular cracks on the road surface.
Longitudinal Cracks: They are the ones that span the length of the road. The causes of them are weak joints or shoddy construction.
Transverse Cracks: This type of crack mainly occurs due to temperature variations, and it quickly runs across the road.
Edge Cracks: As the name suggests, these cracks happen close to the road’s edge. Inadequate support or excessive loads are known to be the primary reasons for them.
Reflection Cracks: These are the ones that appear in a fresh overlay. The worst part is that they emulate pre-existing sublayer fractures underneath it.
Core Causes of Road Cracking

It is proven that all the road cracks arise due to one or more of the following factors:
Load-Induced Stress: Recurring loads, heavy traffic and overweight vehicles can make the pavement structure weak in the long run.
Environmental Effects: The pavement can get compressed and expanded due to light exposure, water penetration, and temperature variations, which eventually leads to resulting in fractures.
Problems with Construction or Materials: If the road has a weak foundation support, lower-quality concrete or asphalt or poor compaction, it may lead to cracking.
Many road cracks get worse because authorities ignore minor fractures in the initial stages. Neglecting tiny signs will end up with water leaking in and undermining the base, causing deterioration to accelerate.
The Risks and Impacts of Road Cracks
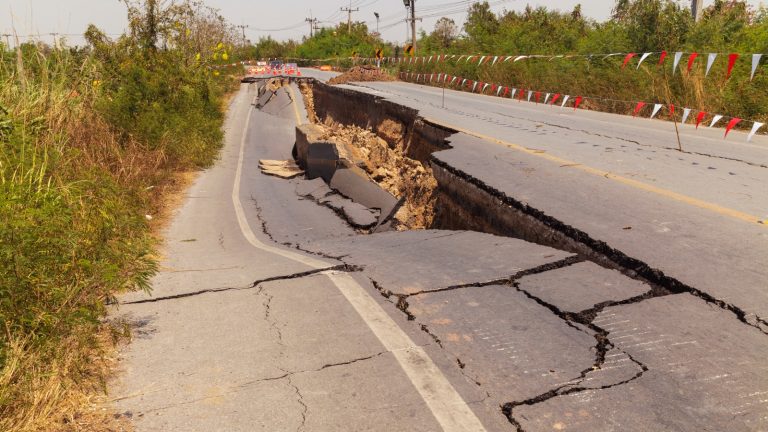

Safety Risks
Road cracks are detrimental in addition to being an inconvenience. Cracks can create uneven surfaces, which can create conditions that compromise driving safety and comfort. Small fissures tend to advance into potholes, which can harm cars and raise the possibility of collisions, particularly for cyclists and motorcyclists.
Economic and Maintenance Consequences
If ignored, even little cracks might routinely progress into expensive repairs. Early crack sealing is demonstrably less capital-intensive than patching huge damaged areas or redoing the entire road. This is where frequent repair can save total costs and greatly increase pavement life.
How Climate or Local Conditions Amplify Cracking

Heat and Sun Exposure – In regions with higher temperatures, asphalt tends to soften. It will eventually lead to breaking if the road is exposed to heavy traffic.
Rain and Moisture – Water penetration is the main reason that erodes the base and subgrade. This causes fractures to spread faster.
Soil and Subgrade Movement- Soft or moving ground ultimately puts a heavy stress on the pavement, and this may cause fractures.
When the authorities select the most effective maintenance and preventive solutions for road cracks, they must initially understand the local circumstances.
Practical Tips to Prevent Road Cracks

The road crack prevention is not that simple as it demands a broad spectrum of requirements, such as adequate design, construction, and maintenance. What works is as follows:
Design and Construction Best Practices
Proper Base and Subgrade – The road development authorities must guarantee that the earth beneath the pavement is firm and resilient. A solid base is important as it can relieve tension on the surface.
Quality Materials- Always better to use asphalt or concrete mixtures as they are known to be the most appropriate for local traffic and various climate circumstances. High-quality materials are not only more durable, but also they are less likely to break.
Drainage Planning – Proper drainage remains at the top of the list as it keeps water from accumulating beneath the pavement. This helps reduce water-induced cracking.
Incorporate Regular Maintenance Strategies
Early Crack Sealing – In the road construction industry, it is a proven strategy to use sealant to fill minor cracks. This will keep water out and prevent additional damage.
Routine Inspections – It is a must to regularly inspect roads for new cracks and damage. There is a high possibility of saving money and eliminating accidents when the authorities detect issues early.
Surface Treatments- One of the most underrated strategies is to use protective layers such as sealcoating or overlays. This aids in avoiding cracking and wear on older pavements.
Localised and Environmental Measures
Traffic Management – Start by restricting or limiting the large vehicle loads on routes that are not suitable for them.
Vegetation Control – Planting huge trees too close to road borders is potentially problematic, as their roots might cause cracks.
Climate adaptation entails using materials and designs that take into account local temperatures, moisture levels, and soil characteristics.
Ask for Expert Advice
- Wide, interconnected cracks, known as alligator cracks.
- Cracks with visible water damage or base failure.
- Repeated or expanding cracks despite regular maintenance.
Spotting Road Cracks Effectively with AI Power

Road cracks happen everywhere, but the good thing is that they are preventable with the right strategies. This is why it is important to comprehend what they are, why they happen, and the risks they pose to ensure long-lasting road networks. In the era of digital transformation, AI can be the best solution to spot road cracks. That is why you need to partner with an industry expert like Tigernix, as we have developed a cutting-edge Smart Transportation Asset Software Suite that is powered by Industry 4.0 technologies to help with road development to maintenance. With AI power, it is not a big deal to ensure a lifespan above 15 years for the roads.